The logistics of getting freight on the right truck on the right road has never been more challenging. In fact, doing it efficiently and on the scale frequently surpasses the ability of even the best freight handlers. We look at the challenges posed by poorly maintained and often chaotic road systems around the world in our piece Mobile Apps in Logistics.
Here we look at automating the incredibly dynamic and difficult task of making sure that the truck being hired is a match for the item being shipped. In this discussion, we examine the problem of identifying truck models merely from their images.
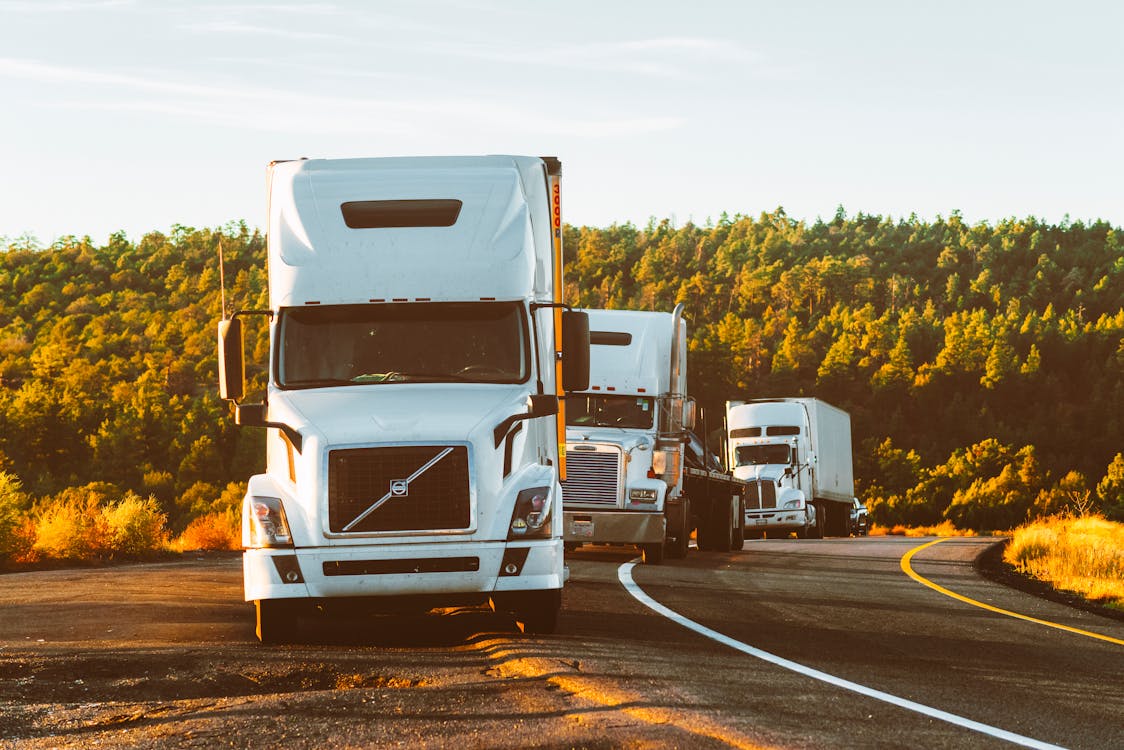
We begin with a discussion of the vast array of trucks employed in the freight industry. The selection of an appropriate truck needs to be done in real-time and from an image of trucks passing down a road or sitting in a yard waiting to be deployed.
After that, we discuss the current state of image recognition, followed by a somewhat more detailed discussion of artificial intelligence open pair and AI closed parent applications. At Faberwork, our model identification system employs TensorFlow and Python.
Truck Model Identification
To the untutored eye, the subtlety of different truck makes and models are largely lost. Yet, these subtleties are of extreme importance in freight selection. The Federal Highway Administration classified commercial trucks by their sizes and characteristics.
Light-duty trucks, medium-duty trucks, and heavy-duty trucks represent broad classes, but each class includes a wide variety of vehicles. Heavy-duty trucks include tractor-trailers and dump trucks. These broad categories are just the beginning.
Heavy-duty trucks, the ones we are often most interested in, have a myriad of other features. These include critical items such as horsepower that can range from 400 to over 600 HP and multiple axles (6x4 or 8x4). They may have sleeper cabs, air suspension, anti-lock braking systems (ABS), traction control, or stability control. These and many other features relate to their efficiency with different-sized loads on various roads.
The identification of truck models from images poses even more challenges. First, trucks appear in different orientations, lighting, and backgrounds, making image differences a significant hurdle. Second, truck models can look very much alike, complicating the process. Finally, effective AI model training requires a substantial dataset with well-annotated labels.
The complexity in truck model types has long posed a challenge to image recognition models. The task is as complex as it is important to logistics, fleet management, and automotive analytics. Fortunately, model development in image recognition has enjoyed substantial progress in developing the tools for precise model identification.
In today's dynamic landscape of computer vision, the ability to discern truck models from images holds significant implications for industries. Employing TensorFlow and Python, developers can construct robust systems capable of accurately identifying various truck models. This article delves into the latest methodologies and enhancements in this domain, elucidating how these tools facilitate precise model identification.
Recent advancements in image recognition leverage deep learning and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), resulting in remarkable strides in accuracy and capability. Key developments include transfer learning, where pre-trained models like InceptionV3, ResNet, and EfficientNet, originally trained on extensive datasets such as ImageNet, accelerate and enhance training for truck model identification. Data augmentation techniques, such as rotation, scaling, and color adjustments, augment the dataset, enriching model generalization. Additionally, fine-tuning pre-trained models to align with the nuanced characteristics of truck images further refines identification accuracy.
Truck Model Identification System with TensorFlow and Python
Building an effective truck model identification system involves a structured approach using TensorFlow and Python. Data collection requires assembling a diverse collection of truck images representing various models. This dataset is then organized into training, validation, and test sets to ensure adequate coverage across different models.
Setting up the environment requires installing TensorFlow and requisite libraries like NumPy to facilitate seamless model development. Data augmentation is implemented using TensorFlow's ImageDataGenerator, applying techniques such as rotations and flips to expand dataset variability and improve model robustness.
Model creation involves constructing a CNN incorporating convolutional, pooling, and dense layers tailored for image classification. The model is trained by compiling it with the Adam optimizer and sparse categorical cross-entropy loss function, using the prepared dataset to learn optimal mappings. Post-training, the model's performance is evaluated on the test set to gauge accuracy and effectiveness.
Models are stored using serialization libraries like Pickle for future reuse and further refined through fine-tuning to enhance accuracy by refining parameters or incorporating new data to adapt to evolving requirements. The models can be further enhanced with more advanced techniques.
Applying the Faberwork model
The Faberwork Truck Identification model is integrated into diverse applications such as trip feasibility assessment, fleet management optimization, and predictive maintenance scheduling.
“By leveraging TensorFlow and Python, developers can create precise systems capable of identifying truck models from images. And the work for our customers continues as technology evolves.”
—Balraj Singh, Software Engineer, Faberwork